Chain¶
If you have worked on LangChain before, you already knows 80% of what chain does. Chain is the stateful orchestrator for agent, which controls when to involve agent in which way. It offers a framework to interact with agents by controlling the information flow. Chain leverages a memory component that memorizes past conversations and any other intermediate steps, such as tool outputs.
For a typical chain, it contains an agent to interact with, list of tools that agent might use
and memory that stored stateful information.
Flow diagram describes the high level picture of the default chain interaction with an agent.
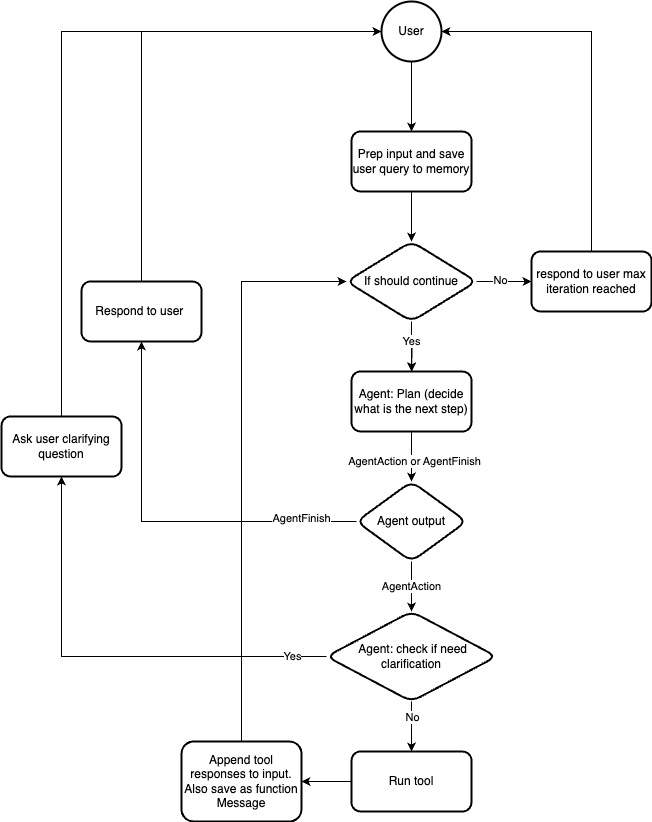
Differences with LangChain¶
To remove abstraction and internal concepts, we expose a more flatten and simplified interface for chain and explained in details below. The main difference is we simply the flow and removed as many internal concepts as possible.
BaseChain and Chain¶
This is the most generic interface for implementing any chain in AutoChain. It contains a few
features user could override. BaseChain is the generic interface where Chain is the default
chain implementation by implementing the only abstract method take_next_step
run¶
this is the entry point to interact with chain with user_query. Because there are often
different ways to interact with the chain, any chain could override the _run function that
handles the business logics for agent interaction, while still be benefited from input and
output standardization provided by the BaseChain.
_run¶
This provide the standard way to manage memories and determines when the agent should stop
answering user query. Most of the time, user could reuse how
we manage memory and just need to change what is the next step agent should do given inputs
including user_query and memories. In that case, user would need to implement the
take_next_step function.
take_next_step¶
This is an abstract method implements the way you would like to interact with agent and asking
agent to come up with the next step. The default implementation is in Chain, where it asks
the agent to plan for next step and execute tools selected by agent
should_answer¶
It is often unclear when agent should stop responding to user query. Sometimes user would just
say "Thank you" in the end but agent might not understand this as end of the conversation, so
it could still try to respond with more contents, even clarifying questions in some cases. By
default, agent will always respond to user until user stops. In the case that is not desired, we
introduce the should_answer step in BaseChain to stop agent from further interaction.